Summary
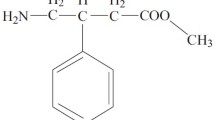
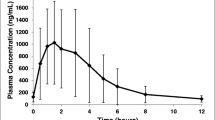
Tranexamic acid 1 g was given intravenously to three healthy volunteers. Plasma concentrations decayed in three monoexponential phases. Most elimination took place during the first eight hours, giving an apparent elimination half-life of approximately two hours. Plasma clearance ranged between 110–116 ml/min. The urinary recovery of tranexamic acid exceeded 95% of the dose. Ten healthy volunteers were given tranexamic acid 2 g orally on an empty stomach, and together with a meal. Food had no influence on the absorption of tranexamic acid, as judged by comparison of the peak plasma concentration, the time required to reach the peak, the AUC from zero to six hours, and the urinary excretion data. The oral bioavailability of tranexamic acid, calculated from 24 h urinary excretion after oral and intravenous administration, was 34% of the dose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson L, Nilsson IM, Colleen S, Granstrand B, Melander B (1968) Role of urokinase and tissue activator in sustaining bleeding and the management thereof with EACA and AMCA. Ann NY Acad Sci 146: 642–656
Boxenbaum HG, Riegelman S, Elashoff RM (1974) Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 2: 123–148
Cormack F, Chakrabarti RR, Jouhar AJ, Fearnley GR (1973) Tranexamic acid in upper gastrointestinal haemmorhage. Lancet 1: 1207–1208
Eriksson O, Kjellman H, Pilbrant Å, Schannong M (1974) Pharmacokinetics of tranexamic acid after intravenous administration to normal volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 7: 375–380
Hedlund PO (1969) Antifibrinolytic therapy with cyklokapron in connection with prostatectomy. A double blind study. Scand J Urol Nephrol 3: 177–182
Metzler CM, Elfring GL, McEwen AJ (1974) A users manual for NONLIN and associated programs. Research Biostatics. Upjohn Co, Kalamazoo, MI
Niazi S (1976) Errors involved in instantaneous intravascular input assumption. J Pharm Sci 65: 750–752
Nilsson L, Rybo G (1967) Treatment of menorrhagia with an antifibrinolytic agent, tranexamic acid (AMCA). A double blind investigation. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 46: 572–580
Tovi D, Nilsson IM, Thulin C-A (1972) Fibrinolysis and subarachnoid haemmorhage. Inhibitory effect of tranexamic acid. A clinical study. Acta Neurol Scand 48: 393–402
Tovi D (1973) The use of antifibrinolytic drugs to prevent early recurrent aneurysmal subarachnoid hemmorhage. Acta Neurol Scand 49: 163–175
Vessman J, Strömberg S (1977) Determination of tranexamic acid in biological material by electron capture gas chromatography after direct derivatization in an aqueous medium. Anal Chem 49: 369–373
Wagner JG and coworkers (1977) Pharmacokinetic parameters estimated from intravenous data by uniform methods and some of their uses. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 5: 161–183
Westlake W (1971) Problems associated with analysis of pharmacokinetic models. J Pharm Sci 60: 882–885
Widlund L, Strömberg S, Hallström H, Osanius B (1979) The disposition of tranexamic acid (AMCA) in different animal species and in man after oral dosage. Scientific Report No. 7999047, Kabi AB, Stockholm
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pilbrant, Å., Schannong, M. & Vessman, J. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of tranexamic acid. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 20, 65–72 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00554669
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00554669