Abstract
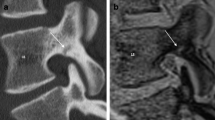
Previous studies have shown the safety and effectiveness of balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs). MRI and particularly the short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequence are very sensitive for detecting vertebral edema as a result of fresh fractures or micro-fractures. Therefore, it has a great therapeutic relevance in differentiating vertebral deformities seen by conventional X-ray and CT scans. Although an MRI scan is expensive, to my knowledge no study has evaluated the benefits of preoperative MRI in evaluating a therapeutic plan for kyphoplasty. This is a prospective study evaluating the benefit of a preoperative MRI scan regarding changes of kyphoplasty therapy. Twenty-eight patients were included in this study. Twenty-four patients were treated by balloon kyphoplasty, in a total of 40 vertebral bodies. The mean age was 73 years. All patients suffered from OVCFs. As a first step, all patients got a CT scan. The individual therapeutic plan was then defined by the patients’ history, complaints and the results of the CT scan. As far as all criteria for kyphoplasty were fulfilled, an MRI examination including the STIR sequences was performed preoperatively. The number of times a change was made in therapy as a result from the additional information from the MRI was then evaluated. By performing a preoperatively MRI examination, the therapy plan was changed in 16 out of 28 (57%) patients. Eight patients underwent additional levels of kyphoplasty at the same procedure. In five patients, lesions were found to be old fractures and therefore were not treated operatively. Two of these patients received no kyphoplasty at all. Another patient only a part of the originally intended levels was treated. The other two cases received a kyphoplasty at different vertebral levels, as these vertebral bodies showed signs of an acute fracture in the MRI scan. Additionally, an incidental diagnosis of carcinoma of the kidney was made in two patients. Kyphoplasty was deferred and they were referred for further evaluation. One patient was found to have an aortic aneurysm. Kyphoplasty was performed and after that the patient was referred in order to treat the aneurysm. This study confirms the diagnostic benefits of an MRI scan before performing a kyphoplasty. For 16 out of 28 patients, the therapeutic plan was changed because of the information obtained by preoperative MRI. Preoperative MRI helped to generate the correct surgical strategy, by demonstrating the correct location of injury and by detecting concomitant diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Berlemann U, Franz T, Orler R, Heini PF (2004) Kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective non-randomized study. Eur Spine J 13:496–501. doi:10.1007/s00586-004-0691-7
Cooper O, Atkinson ES, O`Fallon WM (1992) The incidence of clinically diagnosed vertebral fractures: a population-based study in Rochester, MN, 1985–1989. J Bone Miner Res 7:221–227
Fribourg D, Tang C, Sra P, Delamarter R, Bae H (2004) Incidence of subsequent vertebral fracture after kyphoplasty. Spine 29:2270–2276. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000142469.41565.2a
Gaitanis I, Voronov L, Ghanayem A, Carandang G, Havey R, Zindrick M, Phillips F, Hadjipavlou A, Patwardhan A (2004) An effect of balloon kyphoplasty on the restoration of spinal alignment in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Orthopedic Research Society, San Francisco, March 7–10
Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D (1987) Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplaty. Neurochirurgie 33:166–168
Gangi A, Kastler BA, Dietemann JL (1994) Percutaneous vertebroplasty guided by a combination of CT and fluoroscopy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:83–86
Garfin SR, Yuan HA, Reily ME (2001) New technologies in spine. Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine 26:1511–1515. doi:10.1097/00007632-200107150-00002
Kanis JA, Pitt FA (1992) Epidermiology at osteoporosis. Bone 13:S1–S10. doi:10.1016/8756-3282(92)90189-4
Ledlie J, Renfro M (2003) Balloon kyphoplasty: one-year outcomes in vertebral body height restoration, chronic pain and activity levels. J Neurosurg 98:36–42
Lee YL, Yip KM (1996) The osteoporotic spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res 323:91–97. doi:10.1097/00003086-199602000-00012
Liebermann IH, Dudeney S, Reinhardt MK, Bell G (2001) Initial outcome and efficacy of “kyphoplasty” in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 26:1631–1638. doi:10.1097/00007632-200107150-00026
Lindsay R, Silverman SL, Cooper C (2001) Risk of new vertebral fracture in the year following a fracture. JAMA 285:320–323. doi:10.1001/jama.285.3.320
Magerl F, Aebi M, Gerzbein SD (1994) A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbal injuries. Eur Spine J 3:184–201. doi:10.1007/BF02221591
Masala S, Schillaci O, Massari F, Danieli R, Ursone A, Fiori R, Simonetti G (2005) MRI and bone scan imaging in the preoperative evaluation of painful vertebral fractures treated with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. In Vivo 19:1055–1060
McCredie M (1994) Bladder and kidney cancers. Cancer Surv 19:343–368
Odom GL, Finney W, Woodhall B (1958) Cervical disc lesions. JAMA 166:23–28
Pflugmacher R, Schroeder RJ, Klostermann CK (2006) Incidence of adjacent vertebral fractures in patients treated with balloon kyphoplasty: two years prospective follow-up. Acta Radiol 47:830–840. doi:10.1080/02841850600854928
Pisani P, Bray F, Parkin DM (2002) Estimates of the world-wide prevalence of cancer for 25 sites in the adult population. Int J Cancer 97:72–81. doi:10.1002/ijc.1571
Riggs BL, Melton LJ (1986) Involutional osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 314:1676–1686
Riggs BL, Melton LJ (1995) The worldwide problem of osteoporosis: insight afforded by epidermiology. Bone 17:505S–511S. doi:10.1016/8756-3282(95)00258-4
Silverman A (1992) The clinical consequences of vertebral compression fractions. Bone 13:261–267. doi:10.1016/8756-3282(92)90193-Z
Watts NB, Harris ST, Genant HK (2001) Treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures with percutanous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Osteoporos Int 12:429–437. doi:10.1007/s001980170086
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spiegl, U.J.A., Beisse, R., Hauck, S. et al. Value of MRI imaging prior to a kyphoplasty for osteoporotic insufficiency fractures. Eur Spine J 18, 1287–1292 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-009-1045-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-009-1045-2