Abstract
Introduction
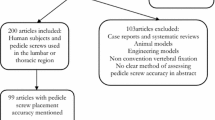
With the advances and improvement of computer-assisted surgery devices, computer-guided pedicle screws insertion has been applied to the lumbar, thoracic and cervical spine. The purpose of the present study was to perform a systematic review of all available prospective evidence regarding pedicle screw insertion techniques in the thoracic and lumbar human spine.
Materials and methods
We considered all prospective in vivo clinical studies in the English literature that assessed the results of different pedicle screw placement techniques (free-hand technique, fluoroscopy guided, computed tomography (CT)-based navigation, fluoro-based navigation). MEDLINE, OVID, and Springer databases were used for the literature search covering the period from January 1950 until May 2010.
Results
26 prospective clinical studies were eventually included in the analysis. These studies included in total 1,105 patients in which 6,617 screws were inserted. In the studies using free-hand technique, the percentage of the screws fully contained in the pedicle ranged from 69 to 94%, with the aid of fluoroscopy from 28 to 85%, using CT navigation from 89 to 100% and using fluoroscopy-based navigation from 81 to 92%. The screws positioned with free-hand technique tended to perforate the cortex medially, whereas the screws placed with CT navigation guidance seemed to perforate more often laterally.
Conclusions
In conclusion, navigation does indeed exhibit higher accuracy and increased safety in pedicle screw placement than free-hand technique and use of fluoroscopy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slomczykowski M, Roberto M, Schneeberger P (1999) Radiation dose for pedicle screw insertion. Fluoroscopic method versus computer-assisted surgery. Spine 24:975–982
Ludwig SC, Kowalski JM, Edwards CC 2nd, Heller JG (2000) Cervical pedicle screws: comparative accuracy of two insertion techniques. Spine 25:2675–2681
Sakai Y, Matsuyama Y, Nakamura H, Katayama Y, Imagama S, Ito Z, Ishiguro N (2008) Segmental pedicle screwing for idiopathic scoliosis using computer-assisted surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech 21:181–186
Laine T, Schlenzka D, Mäkitalo K, Tallroth K, Nolte LP, Visarius H (1997) Improved accuracy of pedicle screw insertion with computer-assisted surgery. A prospective clinical trial of 30 patients. Spine 22:1254–1258
Amiot LP, Lang K, Putzier M, Zippel H, Labelle H (2000) Comparative results between conventional and computer-assisted pedicle screw installation in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spine. Spine 25:606–614
Castro WH, Halm H, Jerosch J, Malms J, Steinbeck J, Blasius S (1996) Accuracy of pedicle screw placement in lumbar vertebrae. Spine 21:1320–1324
Esses SI, Sachs BL, Dreyzin V (1993) Complications associated with the technique of pedicle screw fixation. A selected survey of ABS members. Spine 18:2231–2238
Schwarzenbach O, Berlemann U, Jost B, Visarius H, Arm E, Langlotz F, Nolte LP, Ozdoba C (1997) Accuracy of computer-assisted pedicle screw placement. An in vivo computed tomography analysis. Spine 22:452–458
Welch WC, Subach BR, Pollack IF, Jacobs GB (1997) Frameless stereotactic guidance for surgery of the upper cervical spine. Neurosurgery 40:958–963
Mirza SK, Wiggins GC, Kuntz IV Ch, York JE, Bellabarba C, Knonodi MA, Chapman JR, Shaffrey CI (2003) Accuracy of thoracic vertebral body screw placement using standard fluoroscopy, fluoroscopic image guidance, and computed tomographic image guidance. Spine 28:402–413
Fisher CG, Sahajpal V, Keynan O, Boyd M, Graeb D, Bailey C, Panagiotopoulos K, Dvorak M (2006) Accuracy and safety of pedicle screw fixation in thoracic spine trauma. J Neurosurg Spine 5:520–526
Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Cho YS, Riew D (2004) Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: is it safe? Spine 29:333–342
Tian NF, Xu HZ (2009) Image-guided pedicle screw insertion accuracy: a meta-analysis. Int Orthop 33:895–903
Gertzbein SD, Robbins SE (1990) Accuracy of pedicular screw placement in vivo. Spine 15:11–14
Schizas C, Michel J, Kosmopoulos V, Theumann N (2007) Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw insertion in percutaneous posterior transpedicular stabilization. Eur Spine J 16:613–617
Odgers CJ 4th, Vaccaro AR, Pollack ME, Cotler JM (1996) Accuracy of pedicle screw placement with the assistance of lateral plain radiography. J Spinal Disord 9:334–338
Sim E (1993) Location of transpedicular screws for fixation of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine. Computed tomography of 45 fracture cases. Acta Orthop Scand 64:28–32
Rajan V, Kamath V, Shetty AP, Rajasekaran S (2010) Iso-C3D navigation assisted pedicle screw placement in deformities of the cervical and thoracic spine. Indian J orthop 44:163–168
Modi H, Suh SW, Song HR, Yang JH (2009) Accuracy of thoracic pedicle screw placement in scoliosis using the ideal pedicle entry point during the freehand technique. Int Orthop 33:469–475
Beck M, Mittlmeier T, Gierer P, Harms C, Gradl G (2009) Benefit and accuracy of intraoperative 3D imaging after pedicle screw placement: a prospective study in stabilizing thoracolumbar fractures. Eur Spine J 18:1469–1477
Karapinar L, Erel N, Ozturk H, Altay T, Kaya A (2008) Pedicle screw placement with a free hand technique in thoracolumbar spine: is it safe? J Spinal Disord Tech 21:63–67
Wang HC, Yang YL, Lin WC, Chen WF, Yang TM, Lin YJ, Rau CS, Lee TC (2008) Computer-assisted pedicle screw placement for thoracolumbar spine fracture with separate spinal reference clamp placement and registration. Surg Neurol 69:597–601
Upendra BN, Meena D, Chowdhury B, Ahmad A, Jayaswal A (2008) Outcome-based classification for assessment of thoracic pedicular screw placement. Spine 33:384–390
Rampersaud YR, Lee KS (2007) Fluoroscopic computer-assisted pedicle screw placement through a mature fusion mass: an assessment of 24 consecutive cases with independent analysis of computed tomography and clinical data. Spine 32:217–222
Merloz P, Troccaz J, Vouaillat H, Vasile C, Tonetti J, Eid A, Plaweski S (2007) Fluoroscopy-based navigation system in spine surgery. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 221:813–820
Rampersaud YR, Pik JH, Salonen D, Farooq S (2005) Clinical accuracy of fluoroscopic computer-assisted pedicle screw fixation: a CT analysis. Spine 30:183–190
Vougioukas VI, Weber J, Scheufler KM (2005) Clinical and radiological results after parapedicular screw fixation of the thoracic spine. J Neurosurg Spine 3:283–287
Kuntz C 4th, Maher PC, Levine NB, Kurokawa R (2004) Prospective evaluation of thoracic pedicle screw placement using fluoroscopic imaging. J Spinal Disord Tech 17:206–214
Fu TS, Chen LH, Wong CB, Lai PL, Tsai TT, Niu CC, Chen WJ (2004) Computer-assisted fluoroscopic navigation of pedicle screw insertion: an in vivo feasibility study. Acta Orthop Scand 75:730–735
Halm H, Niemeyer T, Link T, Liljenqvist U (2000) Segmental pedicle screw instrumentation in idiopathic thoracolumbar and lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J 9:191–197
Carl AL, Khanuja HS, Gatto CA, Matsumoto M, vomLehn J, Schenck J, Rohling K, Lorensen W, Vosburgh K (2000) In vivo pedicle screw placement: image-guided virtual vision. J Spinal Disord 13:225–229
Laine T, Lund T, Ylikoski M, Lohikoski J, Schlenzka D (2000) Accuracy of pedicle screw insertion with and without computer assistance: a randomised controlled clinical study in 100 consecutive patients. Eur Spine J 9:235–240
Girardi FP, Cammisa FP Jr, Sandhu HS, Alvarez L (1999) The placement of lumbar pedicle screws using computerised stereotactic guidance. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81:825–829
Merloz P, Tonetti J, Pittet L, Coulomb M, Lavalleé S, Sautot P (1998) Pedicle screw placement using image guided techniques. Clin Orthop Relat Res 354:39–48
Laine T, Mäkitalo K, Schlenzka D, Tallroth K, Poussa M, Alho A (1997) Accuracy of pedicle screw insertion: a prospective CT study in 30 low back patients. Eur Spine J 6:402–405
Rajasekaran S, Vidyadhara S, Ramesh P, Shetty AP (2007) Randomized clinical study to compare the accuracy of navigated and non-navigated thoracic pedicle screws in deformity correction surgeries. Spine 32:56–64
Barr SJ, Schuette AM, Emans JB (1997) Lumbar pedicle screws versus hooks. Results in double major curves in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 22:1369–1379
Broom MJ, Banta JV, Renshaw TS (1989) Spinal fusion augmented by luque-rod segmental instrumentation for neuromuscular scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 71:32–44
Hamill CL, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Chapman MP, Blanke K, Baldus C (1996) The use of pedicle screw fixation to improve correction in the lumbar spine of patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Is it warranted? Spine 21:1241–1249
Kosmopoulos V, Schizas C (2007) Pedicle screw placement accuracy: a meta-analysis. Spine 32:E111–E120
Verma R, Krishan S, Haendlmayer K, Mohsen A (2010) Functional outcome of computer-assisted spinal pedicle screw placement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 23 studies including 5, 992 pedicle screws. Eur Spine J 19:370–375
West JL 3rd, Ogilvie JW, Bradford DS (1991) Complications of the variable screw plate pedicle screw fixation. Spine 16:576–579
Lonstein JE, Denis F, Perra JH, Pinto MR, Smith MD, Winter RB (1999) Complications associated with pedicle screws. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81:1519–1528
Gaines RW Jr (2000) The use of pedicle-screw internal fixation for the operative treatment of spinal disorders. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82-A:1458–1476
Weinstein JN, Spratt KF, Spengler D, Brick C, Reid S (1988) Spinal pedicle fixation: reliability and validity of roentgenogram-based assessment and surgical factors on successful screw placement. Spine 13:1012–1018
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelalis, I.D., Paschos, N.K., Pakos, E.E. et al. Accuracy of pedicle screw placement: a systematic review of prospective in vivo studies comparing free hand, fluoroscopy guidance and navigation techniques. Eur Spine J 21, 247–255 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-2011-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-2011-3