Abstract
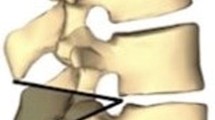
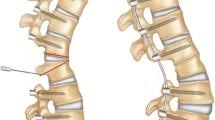
Osteotomies may be life saving procedures for patients with rigid severe spinal deformity. Several different types of osteotomies have been defined by several authors. To correct and provide a balanced spine with reasonable amount of correction is the ultimate goal in deformity correction by osteotomies. Selection of osteotomy is decided by careful preoperative assessment of the patient and deformity and the amount of correction needed to have a balanced spine. Patient’s general medical status and surgeon’s experience levels are the other factors for determining the ideal osteotomy type. There are different osteotomy options for correcting deformities, including the Smith-Petersen osteotomy (SPO), pedicle subtraction osteotomy (PSO), bone-disc-bone osteotomy (BDBO) and vertebral column resection (VCR) providing correction of the sagittal and multiplanar deformity. SPO refers to a posterior column osteotomy in which the posterior ligaments and facet joints are removed and a mobile anterior disc is required for correction. PSO is performed by removing the posterior elements and both pedicles, decancellating vertebral body, and closure of the osteotomy by hinging on the anterior cortex. BDBO is an osteotomy that aims to resect the disc with its adjacent endplate(s) in deformities with the disc space as the apex or center of rotational axis (CORA). VCR provides the greatest amount of correction among other osteotomy types with complete resection of one or more vertebral segments with posterior elements and entire vertebral body including adjacent discs. It is also important to understand sagittal imbalance and the surgeon must consider global spino-pelvic alignment for satisfactory long-term results. Vertebral osteotomies are technically challenging but effective procedures for the correction of severe adult deformity and should be performed by experienced surgeons to prevent catastrophic complications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwab FJ, Smith VA, Biserni M, Gamez L, Farcy JP, Pagala M (2002) Adult scoliosis: a quantitative radiographic and clinical analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27:387–392
Heary RF (2004) Evaluation and treatment of adult spinal deformity. J Neurosurg Spine 1:9–18
Cho W, Lenke LG (2010) Vertebral osteotomies—review of current concepts. Musculoskeletal Rev 5:46–49
Aebi M (2005) The adult scoliosis. Eur Spine J 14:925–948
Silva FE, Lenke LG (2010) Adult degenerative scoliosis: evaluation and management. Neurosurg Focus 28(3):1–10
Birknes JK, White AP, Albert TJ, Shaffrey CI, Harrop JS (2008) Adult degenerative scoliosis a review. Neurosurgery 63(3):94–103
Dorward GI, Lenke GL (2010) Osteotomies in the posterior only treatment of complex adult spinal deformity: a comparative review. Neurosurg Focus 28(3):1–10
Bridwell KH (2006) Decision making regarding Smith-Petersen vs. pedicle subtraction osteotomy vs. vertebral column resection for spinal deformity. Spine 31(19):171–178
Lafage V, Schwab F, Patel A et al (2009) Pelvic tilt and truncal inclination: two key radiographic parameters in the setting of adults with spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:599–606
Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B et al (2010) Adult spinal deformity-postoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:2224–2231
Bernhart M, Bridwell KH (1989) Segmental analysis of the sagittal plane alignment of normal thoracic and lumbar spines and thoracolumbar junction. Spine 14(7):717–721
Ondra SL, Marzouk S, Koski T, Silva F, Salehi S (2006) Mathematical calculation of pedicle subtraction osteotomy size to allow precision correction of fixed sagittal deformity. Spine 25:973–979
Smith-Petersen MN, Larson EB, AuFranc OE (1945) Osteotomy of the spine for correction of flexion deformity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 27:1–11
Ponte A, Vero B, Siccardi GL (1984) Surgical treatment of Scheuermann’s kyphosis. In: Winter RB (ed) Progress in spinal pathology: kyphosis. Aulo Gaggi, Bologna, pp 75–80
Cho KJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke GL, Berra A, Baldus C (2005) Comparison of Smith-Petersen versus pedicle substraction osteotomy for correction of fixed sagittal imbalance. Spine 30(18):2030–2037
Thomasen E (1985) Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 194:142–152
Heining CA (1984) Eggshell procedure. In: Luque ER (ed) Segmental spinal instrumentation. Thorofare, Slack, pp 221–230
Kim JY, Bridwell KH, Lenke GL, Cheh GE, Baldus C (2007) Results of lumbar pedicle substraction osteotomies of fixed sagittal imbalance a minimum 5-year follow-up study. Spine 32(20):2189–2197
Buchowski JM, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Kuhns CA, Lehman RA, Kim JY, Stewart D, Baldus C (2007) Neurologic complications of lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy a 10-year assessment. Spine 32(20):2245–2252
Yang BP, Ondra SL, Chen LA et al (2006) Clinical and radiographic outcomes of thoracic and lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy for fixed sagittal imbalance. J Neurosurg Spine 5:9–17
Ahn UM, Ahn NU, Buchowski JM et al (2002) Functional outcome and radiographic correction after spinal osteotomy. Spine 27:1303–1311
Domanic U, Talu U, Dikici F, Hamzaoglu A (2004) Surgical correction kyphosis; posterior total wedge resection osteotomy in 32 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 75(4):449–455
Hamzaoglu A, Alanay A, Ozturk C, Sarier M, Karadereler S, Ganiyusufoglu K (2011) Posterior vertebral column resection in severe spinal deformities. Spine 36(5):340–344
Ozturk C, Alanay A, Ganiyusufoglu K, Karadereler S, Ulusoy L, Hamzaoglu A (2011) Short term X-ray results of posterior vertebral column resection in severe congenital kyphosis, scoliosis and kyphoscoliosis Spine [Publish Ahead of Print]
MacLennan A (1922) Scoliosis. BMJ 2:865–866
Suk SI, Chung ER, Kim JH et al (2005) Posterior vertebral column resection for severe rigid scoliosis. Spine 30(14):1682–1687
Lenke LG, O’Leary PT, Bridwell KH, Sides BA, Koester LA, Blanke KM (2009) Posterior vertebral column resection for severe pediatric deformity: minimum two-year follow-up of thirty-five consecutive patients. Spine 34:2213–2221
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enercan, M., Ozturk, C., Kahraman, S. et al. Osteotomies/spinal column resections in adult deformity. Eur Spine J 22 (Suppl 2), 254–264 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2313-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2313-0