Abstract
Purpose
Vertebral hemangioma (VH) is virtually vascular malformation, which is usually asymptomatic. Only 3.7 % of VH may become active and symptomatic, and 1 % may invade the spinal canal and/or paravertebral space. Treatment protocols for active or aggressive VHs are still in controversy. Reported treatments include radiotherapy, vertebroplasty, direct alcohol injection, embolization, surgery and a combination of these modalities.

Methods
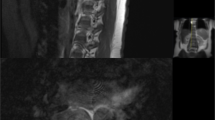
A 41-year-old lady was presented with 18 month history of intermittent back pain. CT revealed T5 osteolytic lesion with epidural and paravertebral extension. The first CT guided biopsy yielded little information.
Results
Histopathological diagnosis of the second biopsy was VH. Vertebroplasty, posterior decompression and fixation were performed followed by postoperative radiotherapy. Her symptoms were resolved immediately after the operation. At 12 months follow-up, no recurrence was detected by CT with contrast enhancement.
Conclusion
Surgical decompression, vertebroplasty and fixation are safe and effective for aggressive VH. More attention is needed in determining the algorithm for the diagnosis and treatment of aggressive VH.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander J, Meir A, Vrodos N et al (2010) Vertebral hemangioma an important differential in the evaluation of locally aggressive spinal lesions. Spine 35(18):E920–E923
Acosta FL Jr, Sanai N, Chi JH et al (2008) Comprehensive management of symptomatic and aggressive vertebral hemangiomas. Neurosurg Clin N Am 19(1):17–29
Acosta FL Jr, Sanai N, Cloyd J et al (2011) Treatment of enneking stage 3 aggressive vertebral hemangiomas with intralesional spondylectomy: report of 10 cases and review of the literature. J Spinal Disord Tech 24:268–275
Bandiera S, Gasbarrini A, De Iure F et al (2002) Symptomatic vertebral hemangioma: the treatment of 23 cases and a review of the literature. Chir Organi Mov 87:1–15
Bas T, Aparisi F, Bas JL (2001) Efficacy and safety of ethanol injections in 18 cases of vertebral hemangioma: a mean follow-up of 2 years. Spine 26(14):1577–1582
Boriani S, Weinstein JN, Biagini R (1997) Primary bone tumors of the spine. Terminology and surgical staging. Spine 22:1036–1044
Doppman JL, Oldfield EH, Heiss JD (2000) Symptomatic vertebral hemangiomas: treatment by means of direct intralesional injection of ethanol. Radiology 214(2):341–348
Fletcher CDM, Unni KK, Mertens F (2002) World Health Organisation classification of tumours Pathology and genetics of tumours of soft tissue and bone. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 310–314
Fox MW, Onofrio BM (1993) The natural history and management of symptomatic and asymptomatic vertebral hemangiomas. J Neurosurg 78:36–45
Heyd R, Seegenschmiedt MH, Rades D et al (2010) Radiotherapy for symptomatic vertebral hemangiomas: results of a multicenter study and literature review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:217–225
Inoue T, Miyamoto K, Kodama H et al (2007) Total spondylectomy of a symptomatic hemangioma of the lumbar spine. J Clin Neurosci 14(8):806–809
Kawahara N, Tomita K, Murakami H et al (2011) Total en bloc spondylectomy of the lower lumbar spine: a surgical techniques of combined posterior-anterior approach. Spine 36:74–82
Krueger EG, Sobel GL, Weinstein C (1961) Vertebral hemangioma with compression of spinal cord. J Neurosurg 18:331–338
Liu XG, Liu ZJ, Dang GT et al (2004) CT-guided percutaneous biopsy of the spine (352 cases review). Chin J Spine Spinal Cord 14:82–85
Robbins LR, Fountain EM (1958) Hemangioma of cervical vertebras with spinal-cord compression. N Engl J Med 258:685–687
Sohn MJ, Lee DJ, Jeon SR et al (2009) Spinal radiosurgical treatment for thoracic epidural cavernous hemangioma presenting as radiculomyelopathy: technical case report. Neurosurgery 64:E1202–E1203
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, L., Liu, C., Yang, S.M. et al. Aggressive vertebral hemangioma of the thoracic spine without typical radiological appearance. Eur Spine J 21, 1994–1999 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2349-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2349-1