Abstract
Purpose
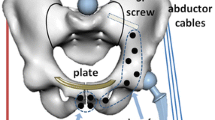
This study investigates the biomechanical stability of a novel technique for symphyseal internal rod fixation (SYMFIX) using a multiaxial spinal screw-rod implant that allows for direct reduction and can be performed percutaneously and compares it to standard internal plate fixation of the symphysis.
Methods
Standard plate fixation (PLATE, n = 6) and the SYMFIX (n = 6) were tested on pelvic composite models with a simulated open book injury using a universal testing machine. On a previously described testing setup, 500 consecutive cyclic loadings were applied with sinusoidal resulting forces of 200 N. Displacement under loading was measured using an optoelectronic camera system and construct rigidity was calculated as a function of load and displacement.
Results
The rigidity of the PLATE construct was 122.8 N/mm (95 % CI: 110.7–134.8), rigidity of the SYMFIX construct 119.3 N/mm (95 % CI: 105.8–132.7). Displacement in the symphyseal area was mean 0.007 mm (95 % CI: 0.003–0.012) in the PLATE group and 0.021 mm (95 % CI: 0.011–0.031) in the SYMFIX group. Displacement in the sacroiliac joint area was mean 0.156 mm (95 % CI: 0.051–0.261) in the PLATE group and 0.120 mm (95 % CI: 0.039–0.201) in the SYMFIX group.
Conclusions
In comparison to standard internal plate fixation for the stabilization of open book pelvic ring injuries, symphyseal internal rod fixation using a multiaxial spinal screw-rod implant in vitro shows a similar rigidity and comparable low degrees of displacement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papakostidis C, Kanakaris NK, Kontakis G, Giannoudis PV. Pelvic ring disruptions: treatment modalities and analysis of outcomes. Int Orthop. 2009;33(2):329–38.
Young JW, Burgess AR, Brumback RJ, Poka A. Pelvic fractures: value of plain radiography in early assessment and management. Radiology. 1986;160(2):445–51.
Rüedi T, Buckley R, Moran C. AO principles of fracture management, vol. 2. 2nd ed. NewYork: Thieme; 2007.
Tile M. Pelvic ring fractures: should they be fixed? J Bone Joint Surg. 1988;70B:1–12.
Putnis SE, Pearce R, Wali UJ, Bircher MD, Rickman MS. Open reduction and internal fixation of a traumatic diastasis of the pubic symphysis: one-year radiological and functional outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(1):78–84.
Adams MR, Scolaro JA, Routt ML Jr. The pubic midline exposure for symphyseal open reduction and plate fixation. J Orthop Traumatol Off J Italian Soc Orthop Traumatol. 2014;15:195–9.
Osterhoff G, Ossendorf C, Wanner GA, Simmen HP, Werner CM. Posterior screw fixation in rotationally unstable pelvic ring injuries. Injury. 2011;42(10):992–6.
Mason WT, Khan SN, James CL, Chesser TJ, Ward AJ. Complications of temporary and definitive external fixation of pelvic ring injuries. Injury. 2005;36(5):599–604.
Kuttner M, Klaiber A, Lorenz T, Fuchtmeier B, Neugebauer R. The pelvic subcutaneous cross-over internal fixator. Unfallchirurg. 2009;112(7):661–9.
Osterhoff G, Tiziani S, Ferguson SJ, Spreiter G, Scheyerer MJ, Spinas GL, Wanner GA, Simmen HP, Werner CM. Mechanical testing of a device for subcutaneous internal anterior pelvic ring fixation versus external pelvic ring fixation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:111.
Scheyerer MJ, Zimmermann SM, Osterhoff G, Tiziani S, Simmen HP, Wanner GA, Werner CM. Anterior subcutaneous internal fixation for treatment of unstable pelvic fractures. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:133.
Vaidya R, Colen R, Vigdorchik J, Tonnos F, Sethi A. Treatment of unstable pelvic ring injuries with an internal anterior fixator and posterior fixation: initial clinical series. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(1):1–8.
Vaidya R, Kubiak EN, Bergin PF, Dombroski DG, Critchlow RJ, Sethi A, Starr AJ. Complications of anterior subcutaneous internal fixation for unstable pelvis fractures: a multicenter study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(8):2124–31.
Ferguson SJ, Winkler F, Nolte LP. Anterior fixation in the osteoporotic spine: cut-out and pullout characteristics of implants. Eur Spine J. 2002;11(6):527–34.
Meissner A, Fell M, Wilk R, Boenick U, Rahmanzadeh R. Biomechanics of the pubic symphysis. Which forces lead to mobility of the symphysis in physiological conditions? Unfallchirurg. 1996;99(6):415–21.
Clements JP, Moriaty N, Chesser TJ, Ward AJ, Cunningham JL. Determination of pelvic ring stability: a new technique using a composite hemi-pelvis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(5):611–6.
Vigdorchik JM, Esquivel AO, Jin X, Yang KH, Onwudiwe NA, Vaidya R. Biomechanical stability of a supra-acetabular pedicle screw Internal Fixation device (INFIX) vs External Fixation and plates for vertically unstable pelvic fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2012;7(1):31.
Vigdorchik JM, Esquivel AO, Jin X, Yang KH, Vaidya R. Anterior internal fixator versus a femoral distractor and external fixation for sacroiliac joint compression and single stance gait testing: a mechanical study in synthetic bone. Int Orthop. 2013;37(7):1341–6.
Dupont WD, Plummer WD. Power and sample size calculations for studies involving linear regression. Control Clin Trials. 1998;19:589–601.
Schwachmeyer V, Damm P, Bender A, Dymke J, Graichen F, Bergmann G. In vivo hip joint loading during post-operative physiotherapeutic exercises. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e77807.
Giraldez-Sanchez MA, Lazaro-Gonzalvez A, Martinez-Reina J, Serrano-Toledano D, Navarro-Robles A, Cano-Luis P, Fragkakis EM, Giannoudis PV. Percutaneous iliosacral fixation in external rotational pelvic fractures. A biomechanical analysis. Injury. 2014;46:327–32.
van Zwienen CM, van den Bosch EW, van Hoek Dijke GA, Snijders CJ, van Vugt AB. Cyclic loading of sacroiliac screws in Tile C pelvic fractures. J Trauma. 2005;58(5):1029–34.
Chong AC, Miller F, Buxton M, Friis EA. Fracture toughness and fatigue crack propagation rate of short fiber reinforced epoxy composites for analogue cortical bone. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(4):487–93.
Osterhoff G, Baumgartner D, Favre P, Wanner GA, Gerber H, Simmen HP, Werner CM. Medial support by fibula bone graft in angular stable plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures: an in vitro study with synthetic bone. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(5):740–6.
Matta JM. Indications for anterior fixation of pelvic fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;329:88–96.
Sagi HC, Papp S. Comparative radiographic and clinical outcome of two-hole and multi-hole symphyseal plating. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(6):373–8.
Cappuccio M, Amendola L, Paderni S, Bosco G, Scimeca G, Mirabile L, Gasbarrini A, De Iure F. Complications in minimally invasive percutaneous fixation of thoracic and lumbar spine fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(6):e729–34.
Ringel F, Stoffel M, Stuer C, Meyer B. Minimally invasive transmuscular pedicle screw fixation of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Neurosurgery. 2006;59(4 Suppl 2):ONS361–6 (discussion ONS366–367).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Synthes (Zuchwil, SO, Switzerland; group PLATE) and Medtronic (Minneapolis, MN, USA; group SYMFIX) for donating the implants that were used for this study.
Conflict of interest
Georg Osterhoff, Simon Tiziani, Carina Hafner, Stephen J. Ferguson, Hans-Peter Simmen, and Clément M. L. Werner declare that they have no conflicts of interests other than the funding of implants as stated in the Acknowledgments.
Compliance with ethical standards
Thus study was conducted in accordance with the ethical guidelines of the European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery. The research did not involve human participants or animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osterhoff, G., Tiziani, S., Hafner, C. et al. Symphyseal internal rod fixation versus standard plate fixation for open book pelvic ring injuries: a biomechanical study. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 42, 197–202 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-015-0529-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-015-0529-5