Abstract
Objective
The multifidus muscle is the only paraspinal lumbar muscle that is innervated by a single nerve root. This study aimes to evaluate if the asymmetry of the multifidus muscle is related to the severity of compression of the nerve root or the duration of radiculopathy.
Methods
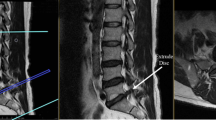
MRI scans of 79 patients with symptomatic single level, unilateral, lumbar radiculopathy were reviewed for this retrospective case series with a nested case–control study. The cross-sectional area (CSA) of the multifidus muscle and the perpendicular distance of the multifidus to the lamina (MLD) were measured bilaterally by two radiologists and set into relation to the severity of nerve compression, duration of radiculopathy and probability of an indication for surgical decompression.
Results
In 67 recessal and 12 foraminal symptomatic nerve root compressions, neither the MLD ratio (severe 1.19 ± 0.55 vs less severe nerve compression: 1.12 ± 0.30, p = 0.664) nor the CSA ratio (severe 1 ± 0.16 vs less severe 0.98 ± 0.13, p = 0.577) nor the duration of symptoms significantly correlated with the degree of nerve compression. MR measurements of multifidus were not different in patients with (n = 20) and those without (n = 59) clinical muscle weakness in the extremity caused by nerve root compression. A MLD >1.5 was, however, associated with the probability of an indication for surgical decompression (OR 3, specificity 92 %, PPV 73 %).
Conclusions
Asymmetry of the multifidus muscle correlates with neither the severity nor the duration of nerve root compression in the lumbar spine. Severe asymmetry with substantial multifidus atrophy seems associated with the probability of an indication of surgical decompression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell WW, Vasconcelos O, Laine FJ. Focal atrophy of the multifidus muscle in lumbosacral radiculopathy. Muscle Nerve. 1998;21(10):1350–3.
Hyun JK, Lee JY, Lee SJ, Jeon JY. Asymmetric atrophy of multifidus muscle in patients with unilateral lumbosacral radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(21):E598–602.
Zhao WP, Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Kanamori M, Kimura T. Histochemistry and morphology of the multifidus muscle in lumbar disc herniation: comparative study between diseased and normal sides. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(17):2191–9.
Yoshihara K, Shirai Y, Nakayama Y, Uesaka S. Histochemical changes in the multifidus muscle in patients with lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(6):622–6.
Kader DF, Wardlaw D, Smith FW. Correlation between the MRI changes in the lumbar multifidus muscles and leg pain. Clin Radiol. 2000;55(2):145–9.
Pfirrmann CW, Dora C, Schmid MR, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N. MR image-based grading of lumbar nerve root compromise due to disk herniation: reliability study with surgical correlation. Radiology. 2004;230(2):583–8.
Hodges P, Holm AK, Hansson T, Holm S. Rapid atrophy of the lumbar multifidus follows experimental disc or nerve root injury. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(25):2926–33.
Kitajima Y, Eguchi Y, Ishibashi E, Nakashita S, Aoki S, Toda S, et al. Age-related fat deposition in multifidus muscle could be a marker for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45(2):218–24.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Source of financial support
Internal institutional financing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farshad, M., Gerber, C., Farshad-Amacker, N.A. et al. Asymmetry of the multifidus muscle in lumbar radicular nerve compression. Skeletal Radiol 43, 49–53 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-013-1748-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-013-1748-7