Abstract
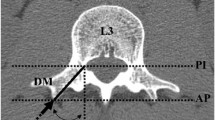
Posterior instrumentation through the pedicle is a common surgery. Understanding the morphometry of the pedicle and the anatomy of adjacent neural structures should help decrease the risk of postoperative complications. T1–L5 segments from 15 sets of human vertebrae were separated into individual vertebrae and the morphometric characteristics of the thoracic and lumbar spine and the safe zone of the pedicle were analyzed. T11–L5 segments from six human cadavers were dissected. Measurements were taken from the pedicle to the dura and nerve roots superiorly, inferiorly, medially, and laterally, and the transverse angles of the nerve roots were measured. Pedicles were widest in L5 and narrowest in T4 in the transverse plane, and widest in T11 or T12 and narrowest in T1 in the sagittal plane. In individual pedicle, the ranges of the safe zone width and height were 3.4–7.7 and 8.6–13.7 mm, respectively, in T1–T10; and 7.2–17.8 and 13.9–16.7 mm, respectively, in T11–L5. The transverse angle of the pedicle decreases progressively from T1 to T12, then increase from L1 to L5. In sagittal angle, the largest angle localized at T2 and the smallest at L5. The mean distances from pedicles to adjacent neural structures were greater superiorly and laterally than inferiorly and medially. The lateral distance between nerve root and the pedicle ranged from 2.4 to 9.6 mm in lumbar spine. This study provides potential safe zones for the application of through-pedicle procedures to help decrease the risk of postoperative complications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belkoff SM, Jasper LE, Stevens SS (2002) An ex vivo evaluation of an inflatable bone tamp used to reduce fractures within vertebral bodies under load. Spine 27:1640–1643
Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Fenton DC, Scribner RM, Reiley ME, Talmadge K (2001) An ex vivo biomechanical evaluation of an inflatable bone tamp used in the treatment of compression fracture. Spine 26:151–156
Berry JL, Moran JM, Berg WS, Steffee AD (1987) A morphometric study of human lumbar and selected thoracic vertebrae. Spine 12:362–367
Boachie-Adjei O, Girardi FP, Bansal M, Rawlins BA (2000) Safety and efficacy of pedicle screw placement for adult spinal deformity with a pedicle-probing conventional anatomic technique. J Spinal Disord 13:496–500
Chen HH, Wang WK,Li KC, Chen TH (2004) Biomechanical effects of the body augmenter for reconstruction of vertebral body. Spine 29:E382–E387
Cottle W, Budney D, Moreau M, Raso J, Greenhill B (1995) A transpedicularly implanted anterior spinal support. J Spinal Disord 8:479–485
Ebraheim NA, Jabaly G, Xu R, Yeasting RA (1997) Anatomic relations of the thoracic pedicle to the adjacent neural structures. Spine 22:1553–1557
Ebraheim NA, Rollins JR, Xu R, Yeasting RA (1996) Projection of the lumbar pedicle and its morphometic analysis. Spine 21:1296–1300
Ebraheim NA, Xu R, Ahmad M, Yeasting RA (1997) Projection of the thoracic pedicle and its morphometric analysis. Spine 22:233–238
Ebraheim NA, Xu R, Darwich M, Yeasting RA (1997) Anatomic relations between the lumbar pedicle and the adjacent neural structures. Spine 22:2338–2341
Esses SI, Sachs BL, Dreyzin V (1993) Complications associated with the technique of pedicle screw fixation. Spine 18:2231–2239
Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D (1987) Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie 33:166–168
Gertzbein SD, Robbins SE (1990) Accuracy of pedicular screw placement in vivo. Spine 15:11–14
Hou S, Hu R, Shi Y (1993) Pedicle morphology of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine in a Chinese population. Spine 18:1850–1855
Krag MH, Weaver DL, Beynnon BD, Haugh LD (1988) Morphometry of the thoracic and lumbar spine related to transpedicular screw placement for surgical spinal fixation. Spine 13:27–32
Lieberman IH, Dudeney S, Reinhardt MK, Bell G (2001) Initial outcome and efficacy of “kyphoplasty” in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 26:1631–1638
Lieberman I, Reinhardt MK (2003) Vertebroplasty and kyphoplsty for osteolytic vertebral collapse. Clin Orthop 415S:176–186
Louis R (1978) Topographic relationships of the vertebral column, spinal cord, and nerve roots. Anat Clin 1:3–12
Matsuzaki H, Tokuhashi Y, Matsumoto F, Hoshino M, Kiuchi T, Toriyama S (1990) Problems and solutions of pedicle screw plate fixation of lumbar spine. Spine 15:1159–1165
Mirkovic SR, Schwartz DG, Glazier KD (1995) Anatomic considerations in lumbar posterolateral percutaneous procedures. Spine 20:1965–1971
Olsewski JM, Simmons EH, Kallen FC, Mendel FC, Severin CM, Berens DL (1990) Morphometry of the lumbar spine: Anatomical perspectives related to transpedicular fixation. J Bone Joint Surg 72A:541–549
Panjabi MM, Takata K, Goel V, Federico D, Oxland T, Duranceau J, Krag M (1991) Thoracic human vertebrae. Quantitative three-dimensional anatomy. Spine 16:888–901
Phillips FM, Ho E, Campbell-Hupp M, McNally T, Wetzel FT, Gupta P (2003) Early radiographic and clinical results of balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 28:2260–2267
Phillips FM (2003) Minimally invasive treatments of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 28:S45–S53
Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C (1986) Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. Clin Orthop 203:7–17
Suk S, Lee CK, Kim W, Chung YJ, Park YB (1995) Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 20:1399–1405
Weinstein JN, Spratt KF, Spengler D, Brick C, Reid S (1988) Spinal pedicle fixation: Reliability and validity of roentgenogram-based assessment and surgical factors on successful screw placement. Spine 13:1012–1018
West JL, Ogilvie JW, Bradford DS (1991) Complications of the variables screw plate pedicle screw fixation. Spine 16:576–579
Zindrick MR, Wiltse LL, Doornik A, Widell EH, Knight GW, Patwardhan AG, Thomas JC, Rothman SL, Fields BT (1987) Analysis of the morphometric characteristics of the thoracic and lumbar pedicles. Spine 12:160–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lien, SB., Liou, NH. & Wu, SS. Analysis of anatomic morphometry of the pedicles and the safe zone for through-pedicle procedures in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Eur Spine J 16, 1215–1222 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-006-0245-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-006-0245-2