Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the relationship between spinopelvic parameters and clinical symptoms for patients with severe isthmic spondylolisthesis.
Methods
A series of spinopelvic parameters were measured in 64 patients with L5 severe isthmic spondylolisthesis. The patients were divided into two groups according to Oswestry score obtained preoperatively, i.e. mild or severe low back pain group. T test was used to compare parameters between two groups, and multiple linear regression analysis was employed to investigate the association between parameters and Oswestry score.
Results
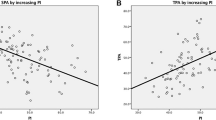
Compared with two group patients, parameters of spondylolisthesis grade, pelvic tilt (PT), lumbar lordosis (LL), T9 tilting angle (T9TA), sacro-femoral horizontal distance (SFHD), distance between perpendicular line through C7 and sacrum (SC7D), pelvic tilt/sacral slope (PT/SS), sacro-femoral horizontal distance/vertical distance (SFHD/SFVD), and lumbar lordosis/thoracic kyphosis (LL/TK) were significantly increased in severe low back pain group, while SS and SFVD were significantly decreased, and no significant difference was found for pelvic incidence (PI) and TK. The statistical analysis showed that spondylolisthesis grade, PT, SC7D, LL, SFHD, PT/SS, SFHD/SFVD, and LL/TK had a significant positive correlation with Oswestry score, with an order of spondylolisthesis grade > PT/SS > SC7D > PT > SFHD/SFVD > SFHD > LL/TK > LL. No significant correlation was found for PI, TK, T9TA with Oswestry score, while SS and SFVD had a significant negative correlation with Oswestry score, with an order of SS > SFVD.
Conclusions
The spinopelvic parameters (spondylolisthesis grade, SS, PT, SC7D, LL, SFVD, SFHD, PT/SS, SFHD/SFVD, LL/TK) are significantly correlated with clinical symptoms of severe isthmic spondylolisthesis in patients. The association of the exacerbation of low back pain with SS (correlation coefficient −0.981, strong) and SFVD (correlation coefficient −0.802, strong) is the most significant correlation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duval-Beaupère G, Robain G (1987) Visualization on full spine radiographs of the anatomical connections of the centre of the segmental body mass supported by each vertebra and measured in vivo. Intern Orthop 11:261–269
Duval-Beaupere G, Schmidt C, Cosson P (1992) A Barycentremetric study of the sagittal shape of spine and pelvis: the conditions required for an economic standing position. Ann Biomed Eng 20:451Y62
Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Berthonnaud E, Labelle H, Weidenbaum M (2006) Sagittal alignment of the spine and pelvis in the presence of L5–S1 isthmic lysis and low-grade spondylolisthesis. Spine 31:2484–2490
Boulay C, Tardieu C, Hecquet J, Benaim C, Mouilleseaux B, Marty C, Prat-Pradal D, Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Pelissier J (2006) Sagittal alignment of spine and pelvis regulated by pelvic incidence: standard values and prediction of lordosis. Eur Spine J 15:415–422
Barrey C, Jund J, Perrin G, Roussouly P (2007) Spinopelvic alignment of patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Neurosurgery 61:981–986
Park SJ, Lee CS, Chung SS, Kang KC, Shin SK (2011) Postoperative changes in pelvic parameters and sagittal balance in adult isthmic spondylolisthesis. Neurosurgery 68:355–363
Mehdian SH, Arun R (2011) A new three-stage spinal shortening procedure for reduction of severe adolescent isthmic spondylolisthesis: a case series with medium- to long-term follow-up. Spine 36:705–711
Min K, Liebscher T, Rothenfluh D (2012) Sacral dome resection and single-stage posterior reduction in the treatment of high-grade high dysplastic spondylolisthesis in adolescents and young adults. Eur Spine J Suppl 6:785–791
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Hecquet J, Marty C (1998) The Incidence, fundamental pelvic parameter for the tridimensionnal regulation of the spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J 7:99–103
Marty C, Boisaubert B, Descamps H, Montigny JP, Legaye J, Hecquet J, Duval-Beaupère G (2002) The sagittal anatomy of the sacrum among young adults, infants and spondylolisthesis patients. Eur Spine J 11:119–125
Tardieu C, Bonneau N, Hecquet J, Boulay C, Marty C, Legaye J, Duval-Beaupère G (2013) How is sagittal balance acquired during bipedal gait acquisition? Comparison of neonatal and adult pelvis in three dimensions. Evolutionary implications. J Hum Evol 6:S0047–2484(13)00134-6
Mac-Thiong JM, Labelle H, Berthonnaud E, Betz RR, Roussouly P (2007) Sagittal spinopelvic balance in normal children and adolescents. Eur Spine J 16:227–234
Schwab F, Lafage V, Patel A, Farcy JP (2009) Sagittal plane considerations and the pelvis in the adult patient. Spine 34:1828–1833
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G (2008) Gravitational forces and sagittal shape of the spine: clinical estimation of their relations. Int Orthop 32:809–816
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G (2005) Sagittal plane alignment of the spine and gravity A radiological and clinical evaluation. Acta Orthop Belg 71:213–220
Hresko MT, Labelle H, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E (2007) Classification of high-grade spondylolisthesis based on pelvic version and spine balance: possible rationale for reduction. Spine 32:2208–2213
Labelle H, Hresko T, Roussouly P (2006) Low-grade spondylolisthesis: how pelvic tilt and sacral slope interact with spinopelvicbalance. In: Proceeding of the 6th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Spine Society, Lac Louise, Canada, March 22–25
Mac-Thiong MJ, Wang Z, de Guise JA, Labelle H (2008) Postural model of sagittal spino-pelvic alignment and its relevance for lumbosacral developmental spondylolisthesis. Spine 33:2316–2325
Labelle H, Mac-Thiong JM, Rousso-uly P (2011) Spino-pelvic sagittal balance of spondylolisthesis: a review and classification. Eur Spine J 5:641–614
Labelle H, Mac-Thiong JM (2011) Pre and post-operative assessment of sagittal balance for high-grade developmental spondylolisthesis. ArgoSpine News J 23:28–32
Mac-Thiong JM, Duong L, Parent S, Hresko MT, Labelle H (2012) Reliability of the Spinal Deformity Study Group Classification of Lumbosacral Spondylolisthesis. Spine 37:95–102
Tanguay F, Labelle H, Wang Z, Mac-Thiong JM (2012) Clinical significance of lumbosacral kyphosis in adolescent spondylolisthesis. Spine 37:304–308
Bourghli A, Aunoble S, Reebye O, Le Huec JC (2011) Correlation of clinical outcome and spinopelvic sagittal alignment after surgical treatment of low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J Suppl 5:663–668
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Wang, B., Yin, B. et al. The relationship between spinopelvic parameters and clinical symptoms of severe isthmic spondylolisthesis: a prospective study of 64 patients. Eur Spine J 23, 560–568 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-3064-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-3064-2