Abstract
Purpose
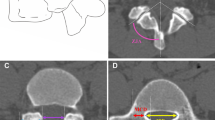
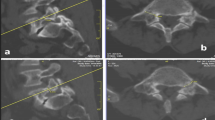
We measured the length, width, height, and angles related to both Meyerding grading system and Marchetti–Bartolozzi classification in L5–S1 spondylolytic spondylolisthesis patients to investigate the anatomical characteristics of fifth lumbar pedicles.
Methods
Seventy patients with L5–S1 spondylolytic spondylolisthesis and general spinal disease were included. Patient attributes, Meyerding grading system and Marchetti–Bartolozzi classification of spondylolisthesis, length, width, height of L4 and L5 pedicle, and the angle between pedicle and vertebral midline were measured. The heights of L5 vertebral body, divided as anterior, mid, and posterior were also measured.
Results
The pedicle is elongated and the angle of the pedicle is wider in cases of L5–S1 spondylolysis. Vertebral body shape was more posteriorly wedged in L5–S1 spondylolysis. Pedicles were more narrow and shorter in L5–S1 spondylolysis.
Conclusions
In L5–S1 spondylolytic spondylolisthesis, a longer screw is suitable for insertion of L5 pedicle and the screw should be inserted more medially compared to patients without spondylolysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajwa NS, Toy JO, Ahn NU (2012) L5 pedicle length is increased in subjects with spondylolysis: an anatomic study of 1072 cadavers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. doi:10.1007/s11999-012-2439-8
Been E, Li L, Hunter DJ, Kalichman L (2011) Geometry of the vertebral bodies and the intervertebral discs in lumbar segments adjacent to spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: pilot study. Eur Spine J 20:1159–1165. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1660-y
Ergun T, Sahin MS, Lakadamyali H (2011) Evaluation of the relationship between L5–S1 spondylolysis and isthmic spondylolisthesis and lumbosacral-pelvic morphology by imaging via 2- and 3-dimensional reformatted computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 35:9–15. doi:10.1097/RCT.0b013e3181f08947
Esses SI, Sachs BL, Dreyzin V (1993) Complications associated with the technique of pedicle screw fixation. A selected survey of ABS members. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 18:2231–2238 (discussion 2238–2239)
Freeman BJ, Licina P, Mehdian SH (2000) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion combined with instrumented postero-lateral fusion: 5-year results in 60 patients. Eur Spine J 9:42–46
Haun DW, Kettner NW (2005) Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: a narrative review of etiology, diagnosis, and conservative management. J Chiropr Med 4:206–217. doi:10.1016/S0899-3467(07)60153-0
Jutte PC, Castelein RM (2002) Complications of pedicle screws in lumbar and lumbosacral fusions in 105 consecutive primary operations. Eur Spine J 11:594–598. doi:10.1007/s00586-002-0469-8
Kalichman L, Kim DH, Li L, Guermazi A, Berkin V, Hunter DJ (2009) Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: prevalence and association with low back pain in the adult community-based population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:199–205. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31818edcfd
Kaplan KM, Spivak JM, Bendo JA (2005) Embryology of the spine and associated congenital abnormalities. Spine J 5:564–576. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2004.10.044
Madan S, Boeree NR (2002) Outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion for spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27:1536–1542
Masharawi Y (2012) Lumbar shape characterization of the neural arch and vertebral body in spondylolysis: a comparative skeletal study. Clin Anat 25:224–230. doi:10.1002/ca.21203
Mehta JS, Kochhar S, Harding IJ (2012) A slip above a slip: retrolisthesis of the motion segment above a spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 21:2128–2133. doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2239-6
Okuda S, Miyauchi A, Oda T, Haku T, Yamamoto T, Iwasaki M (2006) Surgical complications of posterior lumbar interbody fusion with total facetectomy in 251 patients. J Neurosurg Spine 4:304–309. doi:10.3171/spi.2006.4.4.304
Okuyama K, Abe E, Suzuki T, Tamura Y, Chiba M, Sato K (1999) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a retrospective study of complications after facet joint excision and pedicle screw fixation in 148 cases. Acta Orthop Scand 70:329–334
Pawar A, Labelle H, Mac-Thiong JM (2012) The evaluation of lumbosacral dysplasia in young patients with lumbosacral spondylolisthesis: comparison with controls and relationship with the severity of slip. Eur Spine J 21:2122–2127. doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2181-7
Porter RW, Hibbert CS (1984) Symptoms associated with lysis of the pars interarticularis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 9:755–758
Rankine JJ, Dickson RA (2010) Unilateral spondylolysis and the presence of facet joint tropism. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:E1111–E1114. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181de8b72
Steinmann JC, Herkowitz HN, el-Kommos H, Wesolowski DP (1993) Spinal pedicle fixation. Confirmation of an image-based technique for screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 18:1856–1861
Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Lee JH, Cho KJ, Kim HG (1997) Adding posterior lumbar interbody fusion to pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral fusion after decompression in spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 22:210–219 (discussion 219-220)
Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Allardyce TJ et al (1995) Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Part I: morphometric analysis of the thoracic vertebrae. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:1193–1199
Wiltse LL, Newman PH, Macnab I (1976) Classification of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res: 23-29
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, HJ., Park, JY., Chin, DK. et al. Anatomical parameters of fifth lumbar vertebra in L5–S1 spondylolytic spondylolisthesis from a surgical point of view. Eur Spine J 23, 1896–1902 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-3111-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-3111-z