Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to provide evidence for clinical choice of surgical approach in treating spinal tuberculosis, including anterior, posterior and combined approaches (combined anterior and posterior approach).
Methods
A literature search up to June 2015 was performed on PubMed, Embase, Cochrane library, CNKI, Wanfang and Weipu database. Weighted mean differences (WMDs) or risk radios (RRs) and their 95 % confidence intervals (CI) were calculated.
Results
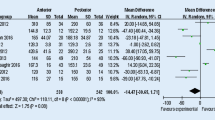
Total 26 studies with 2345 spinal tuberculosis adults were analyzed. Results showed advantages of posterior approach compared with anterior approach in operation time (WMD = 20.91; 95 % CI: 9.05–32.76), blood loss (WMD = 72.32, 95 % CI: 13.87–130.78), correction of angle (WMD = −2.47; 95 % CI: −4.04 to −0.90) and complications (RR = 1.78; 95 % CI: 1.21–2.60), and compared with combined approach in operation time (WMD = −82.76; 95 % CI: −94.38 to −71.14), blood loss (WMD = −263.63; 95 % CI: −336.85 to −190.41), hospital stay [(WMD = −4.60; 95 % CI: −5.10 to −4.10) and complications (RR = 0.36; 95 % CI: 0.23–0.58]. Meanwhile, significantly larger correction of angle (WMD = −2.25; 95 % CI: −4.35 to −0.14; P = 0.04) and less loss of correction (WMD = 3.97; 95 % CI: 2.22–5.72) were found when compared combined approach with anterior approach. However, combined approach had significantly longer operation time (WMD = −41.92; 95 % CI: −52.45 to −31.38) and more blood loss (WMD = −102.18; 95 % CI: −160.45 to −43.91) than anterior approach.
Conclusion
Posterior approach has better clinical outcomes than anterior or combined approach for spinal tuberculosis. However, individual assessment of each case should be considered in the clinical application of these surgical approaches.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garg RK, Somvanshi DS (2011) Spinal tuberculosis: a review. J Spinal Cord Med 34(5):440–454
Rajasekaran S (2012) Kyphotic deformity in spinal tuberculosis and its management. Int Orthop 36(2):359–365
Wang H, Li C, Wang J, Zhang Z, Zhou Y (2012) Characteristics of patients with spinal tuberculosis: seven-year experience of a teaching hospital in Southwest China. Int Orthop 36(7):1429–1434
Issack PS, Boachie-Adjei O (2012) Surgical correction of kyphotic deformity in spinal tuberculosis. Int Orthop 36(2):353–357
Rajasekaran S, Kanna RM, Shetty AP (2014) Pathophysiology and treatment of spinal tuberculosis. JBJS Rev 2(9):e4
Swanson AN, Pappou IP, Cammisa FP, Girardi FP (2006) Chronic infections of the spine: surgical indications and treatments. Clin Orthop Relat Res 444:100–106
Meena S, Mittal S, Chowdhary B (2014) Spinal tuberculosis: which is the best surgical approach? Med Princ Pract 23(1):96–97
Benli IT, Kaya A, Acaroglu E (2007) Anterior instrumentation in tuberculous spondylitis: is it effective and safe? Clin Orthop Relat Res 460:108–116
Molina JE (2013) The posterior approach. In: New techniques for thoracic outlet syndromes. Springer, New York, pp 31–32. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-5471-7_9
Jain AK, Kumar J (2013) Tuberculosis of spine: neurological deficit. Eur Spine J 22(4):624–633
Muheremu A, Niu X, Wu Z, Tian W (2015) Study on anterior and posterior approaches for spinal tuberculosis: a meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 25(Suppl 1):S69–S76. doi:10.1007/s00590-014-1508-y
Erturer E, Tezer M, Aydogan M, Mirzanlı C, Ozturk I (2010) The results of simultaneous posterior–anterior–posterior surgery in multilevel tuberculosis spondylitis associated with severe kyphosis. Eur Spine J 19(12):2209–2215
Zhang HQ, Hu X, Yin X, Chen Y (2015) One-stage combined anterior-posterior approach treatment of multiple cervicothoracic spinal tuberculosis with kyphosis. Int Orthop 39(8):1605–1610. doi:10.1007/s00264-015-2778-7
Liu P, iSun MW, Li SJ, Wang ZH, Ding GQ (2015) A retrospective controlled study of three different operative approaches for the treatment of thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis: 3 years of follow-up. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 128:25–34
Li LT, Xu JZ, Ma Y, Tang DD, Chen YL, Luo F, Li DW, Hou TY, Zhou Q, Dai F (2014) Surgical strategy and management outcomes for adjacent multisegmental spinal tuberculosis: a retrospective study of forty-eight patients. Spine 39(1):E40–E48
Liu J, Wan L, Long X, Huang S, Dai M, Liu Z (2015) Efficacy and safety of posterior versus combined posterior and anterior approach for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis: a meta-analysis. World Neurosurg 83(6):1157–1165. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2015.01.041
Yang P, He X, Li H, Zang Q, Yang B (2014) Clinical efficacy of posterior versus anterior instrumentation for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis in adults: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 9:10
Bent S, Padula A, Avins A (2006) Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing thequality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analysis Brief communication: better ways to question patients about adverse medical events: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 144(4):257–261
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17(1):1–12
Huedo-Medina TB, Sánchez-Meca J, Marín-Martínez F, Botella J (2006) Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? Psychol Methods 11(2):193
Cai M, Li CG (2015) Comparison of three different surgical approaches for the treatment of thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis. China Pract Med 8:73–74. doi:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2015.08.043
Cai XQ (2013) Clinical effect and safety assessment of different surgical approaches of internal fixation in the treatment of patients with thoracolumbal tuberculosis. China Modern Med 20(16):32–34. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4721.2013.16.013
Chen YX (2013) Different surgical approaches for the treatment of lumbar spinal tuberculosis. Shanxi Med J 42(11):683–685. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-9926.2013.11.051
Cui X, Ma YZ, Chen X, Cai XJ, Guo LX, Xue HB, Hu M (2011) Selection and outcome of anterior vs. posterior approach for spinal tuberculosis. Chin J Spine Spinal Cord 21(10):807–812. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-406X.2011.10.05
Dong WP, Cheng XS, Zeng XB (2015) Comparison of clinical effect of three surgical methods in the treatment of tuberculosis of lumbar spine. Anhui Med J 36(2):200–203. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0399.2015.02.022
Garg B, Kandwal P, Nagaraja UB, Goswami A, Jayaswal A (2012) Anterior versus posterior procedure for surgical treatment of thoracolumbar tuberculosis: a retrospective analysis. Indian J Orthop 46(2):165
Hu JT, Chen JS, Qian Z, Yang LL (2015) Comparison of three different surgical approaches for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. Zhejiang J Trauma Surg 20(2):319–321. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-7147.2015.02.055
Lee SH, Sung JK, Park YM (2006) Single-stage transpedicular decompression and posterior instrumentation in treatment of thoracic and thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis: a retrospective case series. J Spinal Disord Tech 19(8):595–602
Li J, Dong J, Li XL, Zhou XG, Ma YQ, Li C (2013) Posterior surgery alone and one-stage combined anterior-posterior surgery for the treatment of thoracic and lumbar tuberculosis. Fudan Univ J Med Sci 40(1):38–43. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2013.01.008
Lu XS, Zhao JM, Peng H, Ling SZ, Wei W (2013) Comparison among five different ways in treatment of thoracic or lumbar tuberculosis. J Spinal Surg 11(2):86–91. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2957.2013.02.006
Luo P, Fang Z, Xiong W, Li GH (2012) Comparative study on the results of three surgical methods for tuberculosis of lumbar spine. J Cervicodynia Lumbodynia 33(1):26–29. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-7234.2012.01.008
Ma SW, Zhang WW, Shen Y, Meng XG, Yao XG, Ding WY, Zhang W (2014) The comparative study of three kinds of operation method and two kinds of internal fixation in-treatment of thoracic and lumbar tuberculosis. J Pract Orthop 20(4):301–304
Ma YZ, Cui X, Li HW, Chen X, Cai XJ, Bai YB (2012) Outcomes of anterior and posterior instrumentation under different surgical procedures for treating thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis in adults. Int Orthop 36(2):299–305
Pu XB, Zhou Q, He QY, Dai F, Xu JZ, Zhang ZH, Branko K (2012) A posterior versus anterior surgical approach in combination with debridement, interbody autografting and instrumentation for thoracic and lumbar tuberculosis. Int Orthop 36(2):307–313
Wang XY, Pang XY, Wu P, Luo CK, Shen XJ (2014) One-stage anterior debridement, bone grafting and posterior instrumentation vs. single posterior debridement, bone grafting, and instrumentation for the treatment of thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis. Eur Spine J 23(4):830–837
Wu GS, Cai XJ, Tian B, Sun JD, Li HW, Jin Q (2012) Clinical effects and analysis of indicators for thoracic and lumbar tuberculosis by different operation approach. J Med Res 41(5):52–55. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-548X.2012.05.017
Xu YT, Lu HG, She YJ, Liu J (2011) Different surgical approaches for lumbar tuberculosis. J Clin Orthop 14(3):265–267. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0287.2011.03.011
Zeng H, Wang X, Pang X, Luo C, Zhang P, Peng W, Wu P, Xu Z (2014) Posterior only versus combined posterior and anterior approaches in surgical management of lumbosacral tuberculosis with paraspinal abscess in adults. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 40(5):607–616
Zhang H, Zhang X, Chen S, Jian X, Zhou J, Lu X, Hu Y (2013) Comparison and observation of surgical approaches and curative effect on 46 cases of thoracolumbar tuberculosis. Med Recapitulate 19(14):2662–2664. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2013.14.060
Zhang HQ, Li JS, Zhao SS, Shao YX, Liu SH, Gao Q, Lin MZ, Liu JY, Wu JH, Chen J (2012) Surgical management for thoracic spinal tuberculosis in the elderly: posterior only versus combined posterior and anterior approaches. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132(12):1717–1723
Zhang HQ, Lin MZ, Li JS, Tang MX, Guo CF, Wu JH, Liu JY (2013) One-stage posterior debridement, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and instrumentation in treatment of lumbar spinal tuberculosis: a retrospective case series. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133(3):333–341
Zhong WY, Xiong GZ, Wang B, Lu C, Dai ZH, Lv GH (2015) Surgical management for thoracic spinal tuberculosis posterior only versus anterior video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. PLoS One 10(3):e0119759
Zhou BY, Huang QH (2014) Comparison of the clinical effect of different surgical methods in the treatment of tuberculosis of lumbar spine. J Cervicodynia Lumbodynia 35(2):118–121. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-7234.2014.02.004
Zhou XZ, Wang GS, Xin JD (2014) Efficacy and options of different surgical approach of spinal tuberculosis. China Cloud Publishing Alliance 14(15):90–90, 92. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-3141.2014.15.061
Yao R, McLachlin SD, Rasoulinejad P, Gurr KR, Siddiqi F, Dunning CE, Bailey CS (2015) Influence of graft size on spinal instability with anterior cervical plate fixation following in vitro flexion-distraction injuries. Spine J. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2015.08.020
Chen C, Zhou J, Guan H (2011) Clinical comparison of three anterior surgeries for cervical spinal instability. Clin Med Eng 12:021
Jain A, Dhammi I, Prashad B, Sinha S, Mishra P (2008) Simultaneous anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation of the tuberculous spine using an anterolateral extrapleural approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(11):1477–1481
Kulkarni SS, Lowery GL, Ross RE, Sankar KR, Lykomitros V (2003) Arterial complications following anterior lumbar interbody fusion: report of eight cases. Eur Spine J 12(1):48–54
Beutler WJ, Sweeney CA, Connolly PJ (2001) Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury with anterior cervical spine surgery: risk with laterality of surgical approach. Spine 26(12):1337–1342
Sahoo MM, Mahapatra SK, Sethi GC, Dash SK (2012) Posterior-only approach surgery for fixation and decompression of thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis: a retrospective study. J Spinal Disord Tech 25(7):E217–E223
Güzey FK, Emel E, Bas NS, Hacisalihoglu S, Seyithanoglu H, Karacor SE, Özkan N, Alatas I, Sel B (2005) Thoracic and lumbar tuberculous spondylitis treated by posterior debridement, graft placement, and instrumentation: a retrospective analysis in 19 cases. J Neurosurg Spine 3(6):450–458
Tosun B, Erdemir C, Yonga Ö, Selek Ö (2014) Surgical treatment of thoracolumbar tuberculosis: a retrospective analysis of autogenous grafting versus expandable cages. Eur Spine J 23(11):2299–2306
Sundararaj G, Behera S, Ravi V, Venkatesh K, Cherian V, Lee V (2003) Role of posterior stabilisation in the management of tuberculosis of the dorsal and lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85(1):100–106
Chen W-J, Wu C-C, Jung C-H, Chen L-H, Niu C-C, Lai P-L (2002) Combined anterior and posterior surgeries in the treatment of spinal tuberculous spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 398:50–59
Huang Q-S, Zheng C, Hu Y, Yin X, Xu H, Zhang G, Wang Q (2009) One-stage surgical management for children with spinal tuberculosis by anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation. Int Orthop 33(5):1385–1390
Vargas LA, Fernández CC, Panadero UT, Aracil GC, Garbizu VJ, González RR (2014) Anterior and anterolateral approach in the treatment of thoracic and lumbar vertebral metastasis causing spinal cord compression. Neurocirugia (Asturias, Spain) 26(3):126–136
Mehta JS, Bhojraj SY (2001) Tuberculosis of the thoracic spine. A classification based on the selection of surgical strategies. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83(6):859–863
Takahata M, Ito M, Abumi K, Kotani Y, Sudo H, Minami A (2008) Clinical results and complications of circumferential spinal cord decompression through a single posterior approach for thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine 33(11):1199–1208
Ikard RW (2006) Methods and complications of anterior exposure of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Arch Surg 141(10):1025–1034
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all respondents of the study and all the people who give the help for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, P., Zang, Q., Kang, J. et al. Comparison of clinical efficacy and safety among three surgical approaches for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J 25, 3862–3874 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4546-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4546-9