Abstract
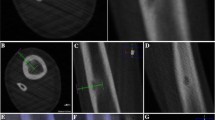
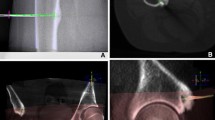
Osteoid osteoma is a relatively common benign skeletal tumor. The traditional standard treatment has been surgical resection of the nidus. Recently, computed tomography (CT)-guided radiofrequency ablation (RFA) has gained favor as a more precise alternative due to potentially less bone destruction. However, CT-guided RFA is limited in treatment for osteoid osteoma involving complex anatomic structures such as cervical spine, pelvis, or scapula because of difficulty in approach and proximity to neurovascular structures. To solve this problem, we investigated RFA using a new real-time three-dimensional fluoroscopic navigation system. We report its technical procedure and use in a rare case of osteoid osteoma of the scapula.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Motamedi D, Learch TJ, Ishimitsu DN, Motamedi K, Katz MD, Brien EW et al (2009) Thermal ablation of osteoid osteoma: overview and step-by-step guide. Radiographics 29:2127–2141
Kransdorf MJ, Stull MA, Gilkey FW, Moser RP Jr (1991) Osteoid osteoma. Radiographics 11:671–696
Virayavanich W, Singh R, O’Donnell RJ, Horvai AE, Goldsby RE, Link TM (2010) Osteoid osteoma of the femur in a 7-month-old infant treated with radiofrequency ablation. Skeletal Radiol 39:1145–1149
Soong M, Jupiter J, Rosenthal D (2006) Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in the upper extremity. J Hand Surg Am 31:279–283
Hoffmann RT, Jakobs TF, Kubisch CH, Trumm CG, Weber C, Duerr HR et al (2010) Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of osteoid osteoma-5-year experience. Eur J Radiol 73:374–379
Mylona S, Patsoura S, Galani P, Karapostolakis G, Pomoni A, Thanos L (2010) Osteoid osteomas in common and in technically challenging locations treated with computed tomography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Skeletal Radiol 39:443–449
Busser WM, Hoogeveen YL, Veth RP, Schreuder HW, Balguid A, Renema WK et al (2010) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteomas with use of real-time needle guidance for accurate needle placement: a pilot study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34:180–183
Lindner NJ, Ozaki T, Roedl R, Gosheger G, Winkelmann W, Wortler K (2001) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in osteoid osteoma. J Bone Jt Surg Br 83:391–396
Rosenthal DI, Hornicek FJ, Torriani M, Gebhardt MC, Mankin HJ (2003) Osteoid osteoma: percutaneous treatment with radiofrequency energy. Radiology 229:171–175
Vanderschueren GM, Taminiau AH, Obermann WR, van den Berg-Huysmans AA, Bloem JL (2004) Osteoid osteoma: factors for increased risk of unsuccessful thermal coagulation. Radiology 233:757–762
Mosheiff R, Liebergall M, Ziv I, Amir G, Segal D (1991) Osteoid osteoma of the scapula. A case report and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res 262:129–131
Lyon C, Buckwalter J (2008) Case report: full-thickness skin necrosis after percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of a tibial osteoid osteoma. Iowa Orthop J 28:85–87
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MPEG 48030 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, K., Myoui, A., Hashimoto, N. et al. Radiofrequency ablation for treatment for osteoid osteoma of the scapula using a new three-dimensional fluoroscopic navigation system. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24, 231–235 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-013-1180-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-013-1180-7