Abstract
Background
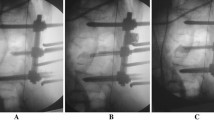
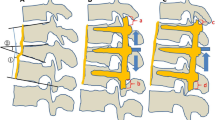
The conventional surgical treatment for thoracolumbar burst fractures is physically invasive for the patient and also causes problems such as the sacrifice of healthy mobile segments to stabilize the fracture site. We performed a procedure for the treatment of fresh thoracolumbar burst fractures by combining percutaneous short pedicle screw fixation and vertebroplasty with transpedicular intracorporeal hydroxyapatite blocks grafting.
Methods
Patients with type A3 fresh thoracolumbar burst fractures with no or mild neurological symptoms were treated using temporary posterior fixation without fusion. Consecutive 21 patients were studied, with a mean age of 45.4 years (range 23–73) and a mean follow-up period of 21.9 months (range 15–25). We evaluated operative time, estimated blood loss, low back pain on a visual analogue scale, change in the kyphotic angle, correction loss, bone union, and complications.
Results
The average operative time was 95.7 min (range 69–143), and the average blood loss was 38.6 mL (range 10–130). The average correction angle was 9.6°. There were slight correction losses of height of the vertebral bodies. Bone union was obtained in all patients, with no instrumentation failures. Our procedure resulted in no surgery-related complications.
Conclusions
For the treatment of type A3 fresh thoracolumbar burst fractures, this method is less invasive and can preserve the adjacent healthy mobile segment. Our treatment is an optional therapeutic strategy for patients with thoracolumbar burst fractures and is a good option particularly for young adult patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denis F, Armstrong GW, Searls K, Matta L (1984) Acute thoracolumbar burst fractures in the absence of neurologic deficit. a comparison between operative and nonoperative treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 189:142–149
Denis F (1983) The three column spine and its significant in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spine injuries. Spine 8:817–831
Kaneda K, Abumi K, Fujiya M (1984) Burst fractures with neurologic deficits of the thoracolumbar-lumbar spine. result of anterior decompression and stabilization with anterior instrumentation. Spine 9:788–795
Magerl F, Aebi M, Gertzbein SD, Harms J, Nazarian S (1994) A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries. Eur Spine J 3:184–201
Beringer W, Potts E, Khairi S, Mobasser JP (2007) Percutaneous pedicle screw instrumentation for temporary internal bracing of nondisplaced bony chance fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech 20:242–247
Blondel B, Fuentes S, Pech-Gourg G, Adetchessi T, Tropiano P, Dufour H (2011) Percutaneous management of thoracolumbar burst fractures: evolution of techniques and strategy. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 97:527–532
Fuentes S, Blondel B, Metellus P, Metellus P, Gaudart J, Adetchessi T, Dufour H (2010) Percutaneous kyphoplasty and pedicle screw fixation for the management of thoraco-lumbar burst fractures. Eur Spine J 19:1281–1287
Korovessis P, Hadjipavlou A, Repantis T (2008) Minimal invasive short posterior instrumentation plus balloon kyphoplasty with calcium phosphate for burst and severe compression lumbar fractures. Spine 33:658–667
Maciejczak A, Barnas P, Dudziak P, Jaqiello-Bajer B, Litwora B, Sumara M (2007) Posterior keyhole corpectomy with percutaneous pedicle screw stabilization in the surgical management of lumbar burst fracture. Neurosurgery 60:232–241
Ni WF, Huang YX, Chi YL, Xu HZ, Lin Y, Wang XY, Huang QS, Mao FM (2010) Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for neurologic intact thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech 23:530–537
Rampersaud YR, Annand N, Dekutoski MB (2006) Use of minimally invasive surgery techniques in the management of thoracolumbar trauma. Spine 31:S96–S102
Sahin S, Resnick DK (2005) Minimally incisional stabilization of unstable L5 burst fracture. J Spinal Disord Tech 18:455–457
Toyone T, Tanaka T, Kato D, Kaneyama R, Otsuka M (2006) The treatment of acute thoracolumbar burst fractures with transpedicular intracorporeal hydroxyapatite grafting following indirect reduction and pedicle screw fixation: a prospective study. Spine 31:E208–E214
Dai LY, Jiang LS, Jiang SD (2008) Conservative treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: a long-term follow-up results with special reference to the load sharing classification. Spine 33:2536–2544
Rajasekaran S (2010) Thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurological deficit: the role for conservative treatment. Eur Spine J 19(Suppl 1):S40–S47
Weninger P, Schultz A, Hertz H (2009) Conservative management of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine compression and burst fractures: functional and radiographic outcomes in 136 cases treated by closed reduction and casting. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129:207–219
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takami, M., Yamada, H., Nohda, K. et al. A minimally invasive surgery combining temporary percutaneous pedicle screw fixation without fusion and vertebroplasty with transpedicular intracorporeal hydroxyapatite blocks grafting for fresh thoracolumbar burst fractures: prospective study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24 (Suppl 1), 159–165 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-013-1266-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-013-1266-2