Abstract
Background
Although unilateral laminectomy and bilateral decompression (ULBD) is effective in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis (DSPL), few reports have compared the outcomes of ULBD and instrumented fusion for the treatment of DSPL. We describe here the clinical and radiological outcomes of ULBD and instrumented fusion surgery for the treatment of DSPL after a minimum 3-year follow-up.
Methods
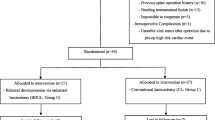
We retrospectively analyzed the outcomes of 47 DSPL patients with radicular pain who underwent ULBD or instrumented fusion between January 2005 and December 2007. Clinical outcomes were assessed using the numeric rating scale (NRS) for back and leg pain, the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), and Short Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36). Radiological outcomes of ULBD were analyzed by determining changes in slippage, disc height translation, and angular difference on simple and dynamic X-rays.
Results
The mean NRS of back pain showed a significantly greater decrease in the fusion than the ULBD group, whereas the mean NRS of leg pain, mean ODI, and mean physical component summary and mental component summary of the SF-36 decreased similarly in the ULBD and fusion groups. Radiologically, the ULBD group showed a 2.1 ± 3.10% change in mean slippage, a 0.15 ± 1.58 mm change in mean translation, a -0.91 ± 4.48° change in mean angular difference, and a -1.83 ± 1.69 mm change in mean disc height. In the ULBD group, three patients had residual pain and three had recurrent pain. In comparison, no patient in the fusion group reported residual pain, whereas five patients experienced recurrent radicular pain caused by adjacent segmental disease.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that ULBD is the recommendable procedure for the treatment of patients with grade I DSPL who have mainly radicular pain. Although the two groups showed similar clinical outcomes overall, radiological degeneration was not as serious after ULBD treatment. In our analysis, foraminal stenosis is a contraindication for ULBD in the treatment of grade I DSPL.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Booth KC, Bridwell KH, Eisenberg BA, Baldus CR, Lenke LG (1999) Minimum 5-year results of degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and instrumented posterior fusion. Spine 24(16):1721–1727
Bridwell KH, Sedgewick TA, O’Brien MF, Lenke LG, Baldus C (1993) The role of fusion and instrumentation in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord 6(6):461–472
Çavuşoğlu H, Kaya RA, Türkmenoglu ON, Tuncer C, Çolak İ, Aydın Y (2007) Midterm outcome after unilateral approach for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis: 5-year prospective study. Eur Spine J 16(12):2133–2142
Cinotti G, Postacchini F, Fassari F, Urso S (1997) Predisposing factors in degenerative spondylolisthesis. A radiographic and CT study. Int Orthop 21(5):337–342
Costa F, Sassi M, Cardia A, Ortolina A, De Santis A, Luccarell G, Fornari M (2007) Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: analysis of results in a series of 374 patients treated with unilateral laminotomy for bilateral microdecompression. J Neurosurg Spine 7(6):579–586
Epstein NE (1998) Decompression in the surgical management of degenerative spondylolisthesis: advantages of a conservative approach in 290 patients. J Spinal Disord 11(2):116–123
Epstein NE (2002) Foraminal and far lateral lumbar disc herniations: surgical alternatives and outcome measures. Spinal Cord 40(10):491–500
Feffer HL, Wiesel SW, Cuckler JM, Rothman RH (1985) Degenerative spondylolisthesis. To fuse or not to fuse. Spine 10(3):287–289
Fischgrund JS, Mackay M, Herkowitz HN, Brower R, Montgomery DM, Kurz LT (1997) 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine 22(24):2807–2812
Ghogawala Z, Benzel EC, Amin-Hanjani S, Barker FG, Harrington JF, Magge SN, Strugar J, Coumans JV, Borges LF (2004) Prospective outcomes evaluation after decompression with or without instrumented fusion for lumbar stenosis and degenerative Grade I spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine 1(3):267–272
Grobler LJ, Robertson PA, Novotny JE, Ahern JW (1993) Decompression for degenerative spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis at L4-5. The effects on facet joint morphology. Spine 18(11):1475–1482
Herkowitz HN (1995) Spine update. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine 20(9):1084–1090
Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT (1991) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. A prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73(6):802–808
Herron LD, Trippi AC (1989) L4-5 degenerative spondylolisthesis. The results of treatment by decompressive laminectomy without fusion. Spine 14(5):534–538
Kettler A, Wilke HJ (2006) Review of existing grading systems for cervical or lumbar disc and facet joint degeneration. Eur Spine J 15(6):705–718
Konno S, Kikuchi S (2000) Prospective study of surgical treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparison between decompression alone and decompression with graf system stabilization. Spine 25(12):1533–1537
Kristof RA, Aliashkevich AF, Schuster M, Meyer B, Urbach H, Schramm J (2002) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis-induced radicular compression: nonfusion-related decompression in selected patients without hypermobility on flexion-extension radiographs. J Neurosurg 97(3 Suppl):281–286
Mardjetko SM, Connolly PJ, Shott S (1994) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. A meta-analysis of literature 1970-1993. Spine 19(20 Suppl):2256S–2265S
Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Morizono Y, Masuda A, Demirtas AM (1990) Natural history of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Pathogenesis and natural course of the slippage. Spine 15(11):1204–1210
McCulloch JA (1998) Microdecompression and uninstrumented single-level fusion for spinal canal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 23(20):2243–2252
McCulloch JA, Young PA (1998) Essentials of spinal microsurgery. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia
Mimura M, Panjabi MM, Oxland TR, Crisco JJ, Yamamoto I, Vasavada A (1994) Disc degeneration affects the multidirectional flexibility of the lumbar spine. Spine 19(12):1371–1380
Mochida J, Suzuki K, Chiba M (1999) How to stabilize a single level lesion of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 368:126–134
Niggemeyer O, Strauss JM, Schulitz KP (1997) Comparison of surgical procedures for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a meta-analysis of the literature from 1975 to 1995. Eur Spine J 6(6):423–429
Nork SE, Hu SS, Workman KL, Glazer PA, Bradford DS (1999) Patient outcomes after decompression and instrumented posterior spinal fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 24(6):561–569
Oertel MF, Ryang Y-M, Korinth MC, Gilsbach JM, Rohde V (2006) Long-term results of microsurgical treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis by unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression. Neurosurgery 59(6):1264–1270
Palmer S, Turner R, Palmer R (2002) Bilateral decompressive surgery in lumbar spinal stenosis associated with spondylolisthesis: unilateral approach and use of a microscope and tubular retractor system. Neurosurg Focus 13(1):E4
Papavero L, Thiel M, Fritzsche E, Kunze C, Westphal M, Kothe R (2009) Lumbar spinal stenosis: prognostic factors for bilateral microsurgical decompression using a unilateral approach. Neurosurgery 65(6 Suppl):182–187
Park JH, Bae CW, Jeon SR, Rhim SC, Kim CJ, Roh SW (2010) Clinical and radiological outcomes of unilateral facetectomy and interbody fusion using expandable cages for lumbosacral foraminal stenosis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 48(6):496–500
Poletti C (1995) Central lumbar stenosis caused by ligamentum flavum:unilateral laminotomy for bilateral ligamentectomy: preliminary report of two cases. Neurosurg 37:343–347
Sasai K, Umeda M, Maruyama T, Wakabayashi E, Iida H (2008) Microsurgical bilateral decompression via a unilateral approach for lumbar spinal canal stenosis including degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine 9(6):554–559
Sengupta DK, Herkowitz HN (2003) Lumbar spinal stenosis. Treatment strategies and indications for surgery. Orthop Clin North Am 34(2):281–295
Spetzger U, Bertalanffy H, Reinges MH, Gilsbach JM (1997) Unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. Part II: Clinical experiences. Acta Neurochir (Wein) 139(5):397–403
Toyoda H, Nakamura H, Konishi S, Dohzono S, Kato M, Matsuda H (2011) Clinical outcome of microsurgical bilateral decompression via unilateral approach for lumbar canal stenosis: minimum five-year follow-up. Spine 36(5):410–415
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.H., Hyun, SJ., Roh, S.W. et al. A comparison of unilateral laminectomy with bilateral decompression and fusion surgery in the treatment of grade I lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. Acta Neurochir 154, 1205–1212 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1394-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1394-1